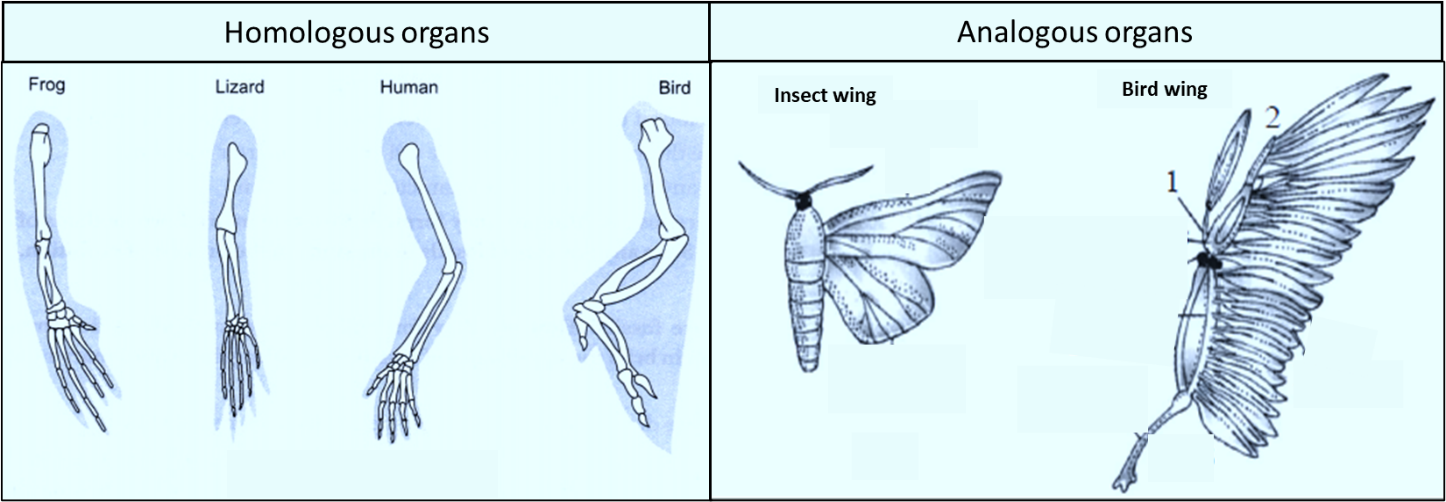
Giving examples of homologous and analogous organs explain what they tell us about the process
Your complex body has over 30 trillion cells, and most of those cells aren't in direct contact with the external environment. 1 A cell deep inside your body—in one of your bones, say, or in your liver—can't get the nutrients or oxygen it needs directly from the environment. How, then, does the body nourish its cells and keep itself running?

48+ Analogous Organs Pictures Gif Petui
Analogous organs are the organs that are different anatomically in structure but perform the same function. They are involved in convergent evolution. Convergent evolution is a form of evolution where other species evolve independently to develop to achieve a similar type of function.

48+ Analogous Organs Pictures Gif Petui
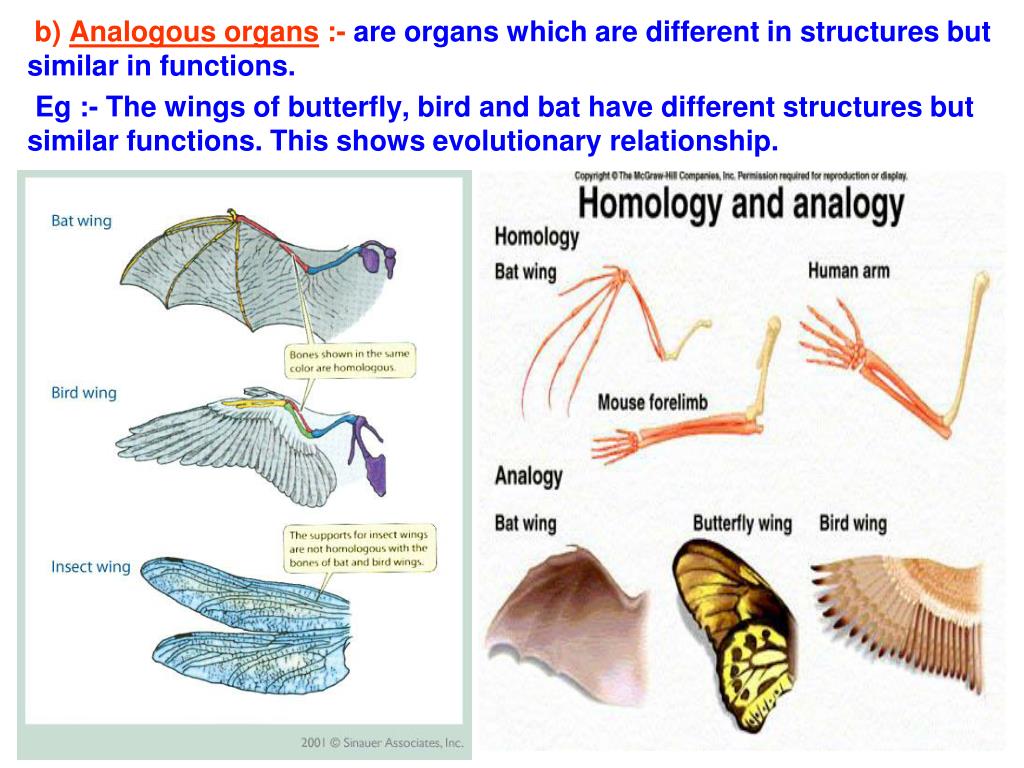
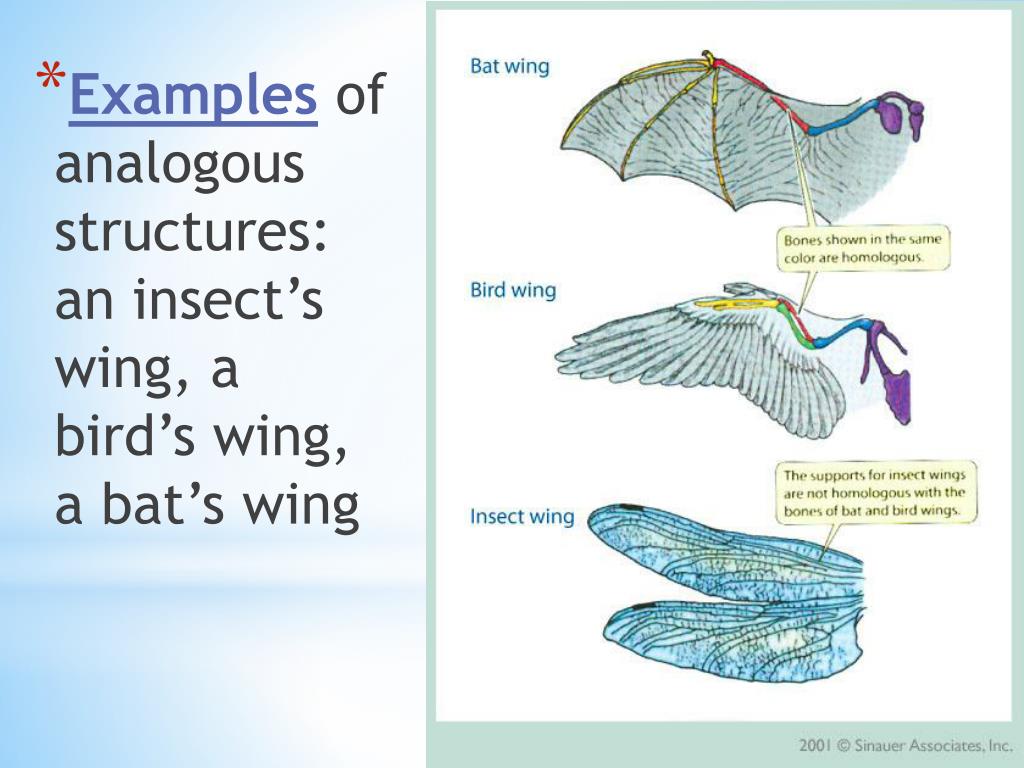
Definition of Analogous Organs: Analogous Organs are defined as the organs of different animals having different anatomy but performing the same function. These animals have different origins and different ancestors. Examples of Analogous organs: Wings of Birds, Bat and Butterfly All these three organs are different in their structures.

Analogous Organs Definition, Examples StudiousGuy
Definition: Structures that have similar functions but with dissimilar evolutionary origins Table of Contents Analogous Structures Definition In evolutionary biology, analogous structures are biological structures having similar or corresponding functions but not from the same evolutionary origin.

29 Organs Homologous Images, Stock Photos & Vectors Shutterstock
Figure 18.5F. 1 18.5 F. 1: Homology vs. analogy: The wings of pterosaurs (1), bats (2), and birds (3) are analogous as wings, but homologous as forelimbs. This is because they are similar characteristically and even functionally, but evolved from different ancestral roots. Paralogous genes often belong to the same species, but not always.
PPT CHAPTER 9 HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID678307
Science ⋅ Biology Anatomical Structures: Homologous, Analogous & Vestigial Updated May 28, 2019 By Lana Bandoim When you compare the wing of a bat to the wing of a bird, you are studying anatomical structures. Anatomy is literally at the core of the structure and function of all organisms.

Human internal organ anatomy gross view Human anatomy picture, Human
Distinguish between homologous and analogous organs. Medium. View solution. The wings of birds are homologous to man's. Easy. View solution. The wings of an insect and a bat exhibit. Easy. View solution. Organisms with homologous structures likely. Medium. View solution.

Class10th Subject Biology lecture 12 ANALOGOUS ORGANS YouTube
August 5, 2023 Binod G C 0 In the diverse tapestry of life, we find fascinating similarities between parts of different animals, even when they aren't closely related. Analogous and Homologous Organs will be described in detail in this article. These resemblances are known as 'analogous' organs, functioning similarly despite looking different.

Revision notes on Heredity and Evolution UNIQUE STUDY POINT
Branching diagram that appeared in Charles Darwin's On the origin of. some physical similarities are analogous: they evolved independently in different organisms because the organisms lived in similar environments or experienced similar. Sometimes a vestigial organ has retained or developed some function — e.g. the mating spurs on boa.

Top 130 + Analogous organs in animals
Over here, these are used for catching insects, here also they catch insects, but the spines are used as a protection. So different functions but same ancestry. Such structures, which have different functions, but same ancestry, we call them homologous, homo-- logous structures. Or homologous function.
Homologous Structures Vs Analogous Structures
Analogous Organs: Definition, Examples, Differences with Homologous Structures and Identification by Dr. Cameron Troup MD in Biology Index They are similar structures that evolved independently in two living organisms to serve the same purpose. Examples of Analog Organs Example 1: Wings through the ages Example 2: The "duck-billed" platypus

Analogous Organs USA, Analogous Organs Manufacturer, Analogous Organs Suppliers and Analogous
1. Homology of Climbing Organs which are all Analogous to Tendrils: Under this head one groups together all types of tendrils and studies the homology of each of them. (1) Tendrils of Vitis are modified apical buds , i.e., homologous to them. (2) Tendrils of Passiflora are homologous to axillary buds. (3) Tendrils of Lathyrus aphaca are.

View Analogous Organs Examples Image Ano
Similar traits can be either homologous or analogous. Homologous structures share a similar embryonic origin; analogous organs have a similar function. For example, the bones in the front flipper of a whale are homologous to the bones in the human arm. These structures are not analogous. The wings of a butterfly and the wings of a bird are.

Make a Venn diagram on homologous and analogus organs Science Heredity and Evolution
Structures that are superficially similar but anatomical dissimilar doing the same function are known as analogous structures. In this article, we look at the various differences between homologous and analogous structures. Homologous vs. Analogous Structures These were a few differences between analogous and homologous structures.

Analogous Biology Structure Free Vector And Clipart Ideas
Analogous organs : The organs which have similar functions but are different in anatomical structures are called analogous organs. Examples of analogous organs are as follows: Wings of an insect and bird. Pectoral fins of shark and flippers of dolphin. Eyes of mammal and octopus.

Analogous Organs YouTube
Human Reproductive Anatomy In general, the reproductive structures in humans can be divided into three main categories: gonads, internal genitalia and external genitalia. The gonads are the organs in which gametes, the cells that fuse in fertilization to form new individuals, develop and mature.